Aria Automation - Prices without Pricing Cards
Overview
Intro
Recently, I was asked to create several Blueprints that would display the resource price at the time of the request through the Service Broker. This had to be accomplished without using VMware Aria Automation Pricing Cards.
The need was to showcase templates with these features:
- Template Azure
- OS: Windows And Linux
- 3 Flavours: Small, Medium and Large
- Managed or Unamanged Machine (SLA)
- In case the vm is managed you have Monitoring SLA - STD or H24
- Template GCP
- OS: Windows And Linux
- 3 Flavours: Small, Medium And Large
- Managed or Unamanged Machine (SLA)
- In case the vm is managed you have Monitoring SLA - STD or H24
- Template vCenter Windows
- OS: Windows 2019 or 2022
- 3 Flavours: Small, Medium And Large
- Managed or Unamanged Machine (SLA)
- In case the vm is managed you have Monitoring SLA - STD or H24
The price varies depending on the Flavour, the operating system, whether it is Managed or Unmanaged, and the type of SLA if the VM is managed.
To enable the most flexible management of future price updates, my solution was to read the prices from a CSV file using PowerShell.
Resource Preparation
Blueprints
Let's take a look at the 3 Blueprints I have prepared:
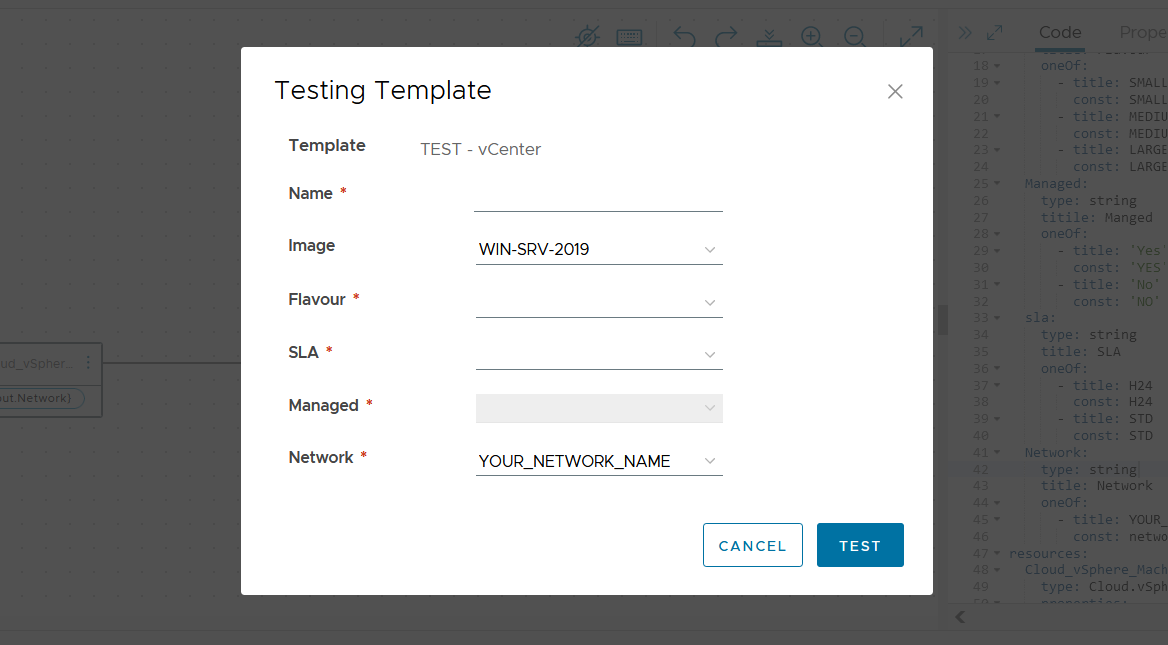
vCenter Windows Blueprint
This Blueprint involves deploying a VM, in this case, a Windows VM, and specifies which vCenter and Storage to allocate it to.
'Managed' refers to a production VM that needs to be monitored, backed up, etc. The SLA should be "Yes" only if the VM is Managed.
The inputs and thus the customization options are:
- Name
- Image
- Flavour
- SLA
- Managed
- Network
1formatVersion: 1
2inputs:
3 Name:
4 type: string
5 title: Name
6 Image:
7 type: string
8 title: Image
9 oneOf:
10 - title: WIN-SRV-2019
11 const: WIN-2019-TEMPLATE
12 - title: WIN-SRV-2022
13 const: WIN-2022-TEMPLATE
14 default: WIN-2019-TEMPLATE
15 Flavour:
16 type: string
17 title: Flavour
18 oneOf:
19 - title: SMALL
20 const: SMALL
21 - title: MEDIUM
22 const: MEDIUM
23 - title: LARGE
24 const: LARGE
25 Managed:
26 type: string
27 titile: Manged
28 oneOf:
29 - title: 'Yes'
30 const: 'YES'
31 - title: 'No'
32 const: 'NO'
33 sla:
34 type: string
35 title: SLA
36 oneOf:
37 - title: H24
38 const: H24
39 - title: STD
40 const: STD
41 Network:
42 type: string
43 title: Network
44 oneOf:
45 - title: YOUR_NETWORK_NAME
46 const: network:YOUR_NETWORK_TAG
47resources:
48 Cloud_vSphere_Machine_1:
49 type: Cloud.vSphere.Machine
50 properties:
51 name: ${input.Name}
52 image: ${input.Image}
53 flavor: ${input.Flavour}
54 Managed: ${input.Managed}
55 sla: ${input.sla}
56 storage:
57 constraints:
58 - tag: Storage:YOUR_STORAGE_TAG
59 networks:
60 - network: ${resource.Cloud_vSphere_Network_1.id}
61 constraints:
62 - tag: Cluster:YOUR_CLUSTER_TAG
63 Cloud_vSphere_Network_1:
64 type: Cloud.vSphere.Network
65 properties:
66 networkType: existing
67 constraints:
68 - tag: ${input.Network}
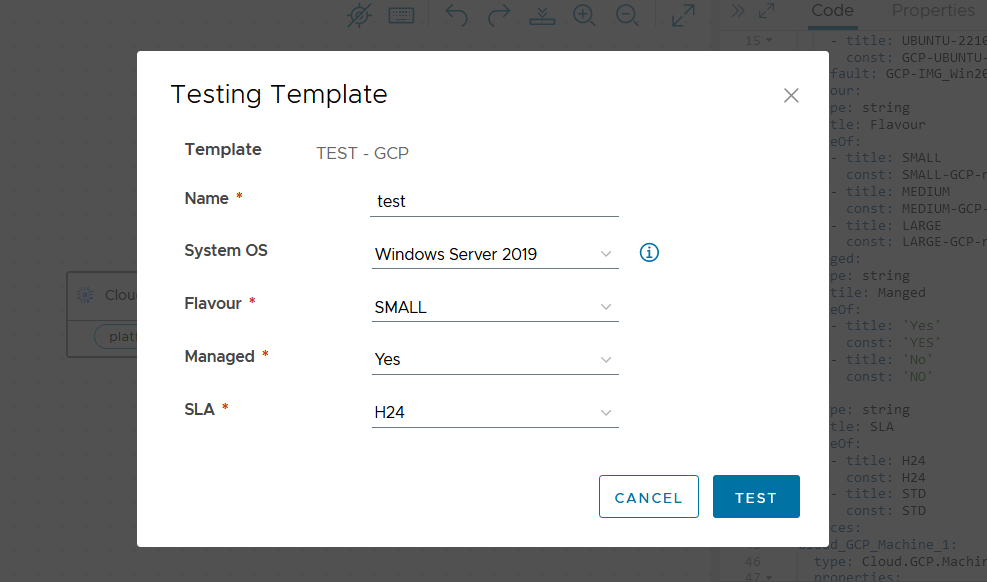
GCP Blueprint
The GCP Blueprint includes Windows and Linux images. In this instance, as it's configured with only one Cloud Account, there's no need to specify details like the cluster. It's sufficient to add the tag associated with the Cloud Zone to the VM.
The inputs are:
- Name
- Image
- Flavour
- SLA
- Managed
1
2formatVersion: 1
3inputs:
4 Name:
5 type: string
6 title: Name
7 Image:
8 type: string
9 title: System OS
10 description: Choose OS
11 oneOf:
12 - title: Windows Server 2022
13 const: GCP-IMG_Win202022
14 - title: Windows Server 2019
15 const: GCP-IMG_Win2019
16 - title: UBUNTU-2210
17 const: GCP-UBUNTU-2210
18 default: GCP-IMG_Win2019
19 Flavour:
20 type: string
21 title: Flavour
22 oneOf:
23 - title: SMALL
24 const: SMALL-GCP-n2-standard-2
25 - title: MEDIUM
26 const: MEDIUM-GCP-n2-standard-4
27 - title: LARGE
28 const: LARGE-GCP-n2-standard-8
29 Managed:
30 type: string
31 titile: Manged
32 oneOf:
33 - title: 'Yes'
34 const: 'YES'
35 - title: 'No'
36 const: 'NO'
37 sla:
38 type: string
39 title: SLA
40 oneOf:
41 - title: H24
42 const: H24
43 - title: STD
44 const: STD
45resources:
46 Cloud_GCP_Machine_1:
47 type: Cloud.GCP.Machine
48 properties:
49 name: ${input.Name}
50 image: ${input.Image}
51 flavor: ${input.Flavour}
52 Managed: ${input.Managed}
53 sla: ${input.sla}
54 networks:
55 - assignPublicIpAddress: false
56 constraints:
57 - tag: platform:gcp #match only one gcp cloud zone and associated network
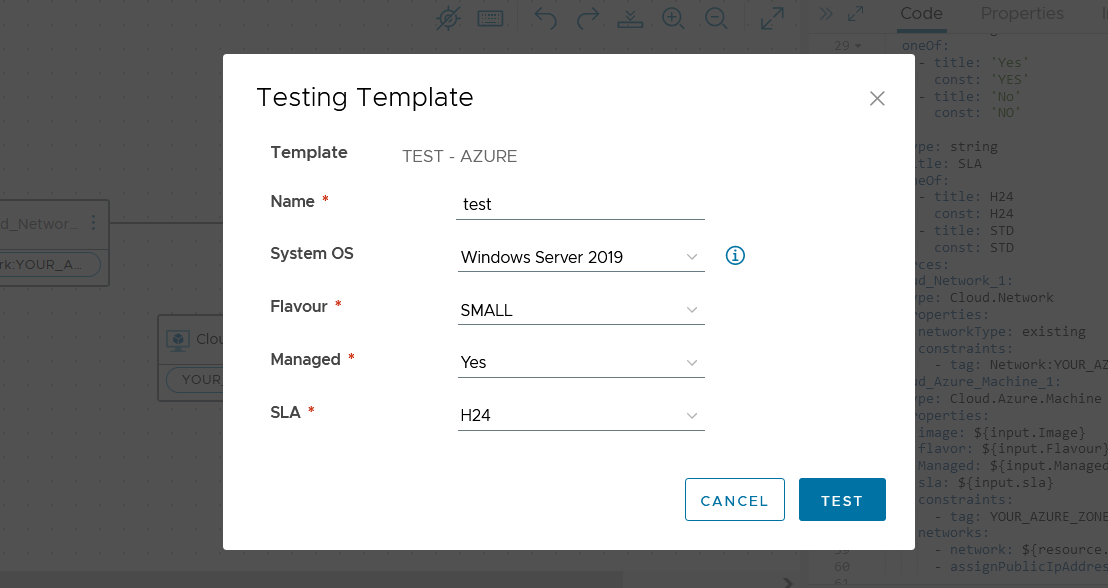
Azure Blueprint
In this case too, I have mapped both Windows and Linux images, and the rest of the template is very similar to the previous ones.
The inputs are the same as for GCP:
- Name
- Image
- Flavour
- SLA
- Managed
1formatVersion: 1
2inputs:
3 Name:
4 type: string
5 title: Name
6 Image:
7 type: string
8 title: System OS
9 description: Choose OS
10 oneOf:
11 - title: Windows Server 2019
12 const: Azure-WindowsServer:2019-Datacenter:lates
13 - title: UBUNTU-2204
14 const: AZURE-UBUNTU-2204
15 default: Azure-WindowsServer:2019-Datacenter:lates
16 Flavour:
17 type: string
18 title: Flavour
19 oneOf:
20 - title: SMALL
21 const: Azure-Standard_B2as_v2
22 - title: MEDIUM
23 const: Azure-Standard_B4als_v2
24 - title: LARGE
25 const: Azure-Standard_B8als_v2
26 Managed:
27 type: string
28 titile: Manged
29 oneOf:
30 - title: 'Yes'
31 const: 'YES'
32 - title: 'No'
33 const: 'NO'
34 sla:
35 type: string
36 title: SLA
37 oneOf:
38 - title: H24
39 const: H24
40 - title: STD
41 const: STD
42resources:
43 Cloud_Network_1:
44 type: Cloud.Network
45 properties:
46 networkType: existing
47 constraints:
48 - tag: Network:YOUR_AZURE_NETWORK_TAG
49 Cloud_Azure_Machine_1:
50 type: Cloud.Azure.Machine
51 properties:
52 image: ${input.Image}
53 flavor: ${input.Flavour}
54 Managed: ${input.Managed}
55 sla: ${input.sla}
56 constraints:
57 - tag: YOUR_AZURE_ZONE_TAG
58 networks:
59 - network: ${resource.Cloud_Network_1.id}
60 - assignPublicIpAddress: false
Warning: All the above examples are for demonstration purposes and must be adapted to your own configuration.
CSV file
The CSV file is quite straightforward, although it may not seem so at first glance. It contains a list of all the various possible combinations of VMs, their specifications, and prices.
As mentioned earlier, the fundamental values on which the price is calculated are:
- Flavour
- SLA
- CloudZone
- OS
- Managed / Unamanged
1Template;SLA;Flavour;OS;cloudzone;managed;vcpu;vram;vm price;managing price
2vCenter managed windows (H24);H24;small;windows;vCenter;yes;2;8;65,22;46,67
3vCenter managed windows (H24);H24;medium;windows;vCenter;yes;4;16;112,81;46,67
4vCenter managed windows (H24);H24;large;windows;vCenter;yes;8;32;207,98;46,67
5vCenter unmanaged windows;NULL;small;windows;vCenter;no;2;8;65,22;null
6vCenter unmanaged windows;NULL;medium;windows;vCenter;no;4;16;112,81;null
7vCenter unmanaged windows;NULL;large;windows;vCenter;no;8;32;207,98;null
8vCenter managed windows (STD);STD;small;windows;vCenter;yes;2;8;65,22;42,50
9vCenter managed windows (STD);STD;medium;windows;vCenter;yes;4;16;112,81;42,50
10vCenter managed windows (STD);STD;large;windows;vCenter;yes;8;32;207,98;42,50
11vCenter managed linux (H24);H24;small;linux;vCenter;yes;2;8;52,57;46,67
12vCenter managed linux (H24);H24;medium;linux;vCenter;yes;4;16;87,51;46,67
13vCenter managed linux (H24);H24;large;linux;vCenter;yes;8;32;157,38;46,67
14vCenter unmanaged linux;NULL;small;linux;vCenter;no;2;8;52,57;null
15vCenter unmanaged linux;NULL;medium;linux;vCenter;no;4;16;87,51;null
16vCenter unmanaged linux;NULL;large;linux;vCenter;no;8;32;157,38;null
17vCenter managed linux (STD);STD;small;linux;vCenter;yes;2;8;52,57;42,50
18vCenter managed linux (STD);STD;medium;linux;vCenter;yes;4;16;87,51;42,50
19vCenter managed linux (STD);STD;large;linux;vCenter;yes;8;32;157,38;42,50
20GCP managed windows (H24);H24;small;windows;GCP;yes;2;8;122,71;46,67
21GCP managed windows (H24);H24;medium;windows;GCP;yes;4;16;239,93;46,67
22GCP managed windows (H24);H24;large;windows;GCP;yes;8;32;474,37;46,67
23GCP unmanaged windows;NULL;small;windows;GCP;no;2;8;122,71;null
24GCP unmanaged windows;NULL;medium;windows;GCP;no;4;16;239,93;null
25GCP unmanaged windows;NULL;large;windows;GCP;no;8;32;474,37;null
26GCP managed windows (STD);STD;small;windows;GCP;yes;2;8;122,71;42,50
27GCP managed windows (STD);STD;medium;windows;GCP;yes;4;16;239,93;42,50
28GCP managed windows (STD);STD;large;windows;GCP;yes;8;32;474,37;42,50
29GCP managed linux (H24);H24;small;linux;GCP;yes;2;8;59,17;46,67
30GCP managed linux (H24);H24;medium;linux;GCP;yes;4;16;112,86;46,67
31GCP managed linux (H24);H24;large;linux;GCP;yes;8;32;220,22;46,67
32GCP unmanaged linux;NULL;small;linux;GCP;no;2;8;59,17;null
33GCP unmanaged linux;NULL;medium;linux;GCP;no;4;16;112,86;null
34GCP unmanaged linux;NULL;large;linux;GCP;no;8;32;220,22;null
35GCP managed linux (STD);STD;small;linux;GCP;yes;2;8;59,17;42,50
36GCP managed linux (STD);STD;medium;linux;GCP;yes;4;16;112,86;42,50
37GCP managed linux (STD);STD;large;linux;GCP;yes;8;32;220,22;42,50
38AZURE managed windows (H24);H24;small;windows;AZURE;yes;2;8;145,31;46,67
39AZURE managed windows (H24);H24;medium;windows;AZURE;yes;4;16;286,08;46,67
40AZURE managed windows (H24);H24;large;windows;AZURE;yes;8;32;567,62;46,67
41AZURE unmanaged windows;NULL;small;windows;AZURE;no;2;8;145,31;null
42AZURE unmanaged windows;NULL;medium;windows;AZURE;no;4;16;286,08;null
43AZURE unmanaged windows;NULL;large;windows;AZURE;no;8;32;567,62;null
44AZURE managed windows (STD);STD;small;windows;AZURE;yes;2;8;145,31;42,50
45AZURE managed windows (STD);STD;medium;windows;AZURE;yes;4;16;286,08;42,50
46AZURE managed windows (STD);STD;large;windows;AZURE;yes;8;32;567,62;42,50
47AZURE managed linux (H24);H24;small;linux;AZURE;yes;2;8;81,83;46,67
48AZURE managed linux (H24);H24;medium;linux;AZURE;yes;4;16;159,11;46,67
49AZURE managed linux (H24);H24;large;linux;AZURE;yes;8;32;313,68;46,67
50AZURE unmanaged linux;NULL;small;linux;AZURE;no;2;8;81,83;null
51AZURE unmanaged linux;NULL;medium;linux;AZURE;no;4;16;159,11;null
52AZURE unmanaged linux;NULL;large;linux;AZURE;no;8;32;313,68;null
53AZURE managed linux (STD);STD;small;linux;AZURE;yes;2;8;81,83;42,50
54AZURE managed linux (STD);STD;medium;linux;AZURE;yes;4;16;159,11;42,50
55AZURE managed linux (STD);STD;large;linux;AZURE;yes;8;32;313,68;42,50
Save this CSV file as prices.csv.
Please note, the prices listed are only examples and do not represent real prices!!
vRo Action Script
The PowerShell script, taking the previously specified data as input, matches it with the data inside the CSV file and then calculates the price, which is then returned as a value.
In this case, the price format uses a comma to separate decimal values. For example, €60,45 (60 euros and 45 cents).
1function Handler($context, $inputs) {
2
3 function Get-CsvData {
4 param (
5 [string]$searchBasePath,
6 [string]$fileName
7 )
8
9 Write-Host "Searching for the file '$fileName' starting from the base path: $searchBasePath"
10
11 # Listing files in the search directory (for debugging)
12 Write-Host "List the files in the base path (for debugging)"
13 Get-ChildItem -Path $searchBasePath -Recurse -File -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Select-Object -First 10 | ForEach-Object { Write-Host $_.FullName }
14
15 # Search for the file in the specified path and its subdirectories
16 $fileFullPath = Get-ChildItem -Path $searchBasePath -Filter $fileName -Recurse -File | Select-Object -First 1
17
18 if ($fileFullPath -eq $null) {
19 Write-Host "File not found: $fileName"
20 return $null
21 }
22
23 Write-Host "File path not found: $($fileFullPath.FullName)"
24
25 # Import data from the found CSV file
26 $data = Import-Csv -Path $fileFullPath.FullName -Delimiter ';'
27 return $data
28 }
29
30 function get-Price {
31 param (
32 [string]$sla,
33 [string]$Flavour,
34 [string]$osInput,
35 [string]$managed,
36 [string]$cloudzone,
37 [string]$filePath
38 )
39
40 # Normalize the value of $Flavour
41 $FlavourNormalized = $null
42 switch -Regex ($Flavour) {
43 "SMALL" { $FlavourNormalized = "small" }
44 "MEDIUM" { $FlavourNormalized = "medium" }
45 "LARGE" { $FlavourNormalized = "large" }
46 }
47
48 # Normalize the value of $os based on the input for linux match lx and ubuntu for windows win and windows
49 $os = $null
50 if ($osInput -match "win|windows") {
51 $os = "windows"
52 } elseif ($osInput -match "lx|ubuntu") {
53 $os = "linux"
54 }
55
56 # Import data from the CSV file
57 $data = Get-CsvData -searchBasePath $filePath -fileName "prices.csv"
58 if ($data -eq $null) {
59 return "File not found"
60 }
61
62 # Data filtering
63 $filteredData = $data | Where-Object {
64 $_.SLA -eq $sla -and $_.Flavour -eq $FlavourNormalized -and
65 $_.OS -eq $os -and $_.managed -eq $managed -and
66 $_.cloudzone -eq $cloudzone
67 } | Select-Object -First 1
68
69 if ($filteredData) {
70 # Use CultureInfo to correctly interpret numbers with a comma
71 $culture = [System.Globalization.CultureInfo]::GetCultureInfo("it-IT")
72
73 # Handle null values for vm price and managing price
74 $priceVmStr = if ($filteredData."vm price" -eq "null" -or $filteredData."vm price" -eq $null) { "0" } else { $filteredData."vm price" }
75 $priceGestioneStr = if ($filteredData."managing price" -eq "null" -or $filteredData."managing price" -eq $null) { "0" } else { $filteredData."managing price" }
76
77 # Try to convert prices into decimal numbers
78 try {
79 $priceVm = [double]::Parse($priceVmStr, [System.Globalization.NumberStyles]::Any, $culture)
80 $priceGestione = [double]::Parse($priceGestioneStr, [System.Globalization.NumberStyles]::Any, $culture)
81 } catch {
82 Write-Host "Error in price conversion: $_"
83 return "Error in converting prices"
84 }
85
86 # Calculate the total cost
87 $priceTotal = "{0:N2}" -f ($priceVm + $priceGestione)
88
89 # Extract details from $filteredData
90 $vcpu = $filteredData.vcpu
91 $vram = $filteredData.vram
92
93 # Create the output string with details
94 $outputString = "• vCPU: $vcpu `n" +
95 "• vRAM: ${vram}GB `n" +
96 "• vDisk Standard Performance: 60 GB `n" +
97 "• OS: $os `n" +
98 "• SLA: $sla `n" +
99 "• vm price: €$priceTotal / month"
100
101 return $outputString
102 }
103
104 return "Can't find prices"
105 }
106
107 # Retrieve inputs from the passed parameters
108 $sla = $inputs.sla
109 $Flavour = $inputs.Flavour
110 $os = $inputs.os
111 $managed = $inputs.managed
112 $cloudzone = $inputs.cloudzone
113
114 # Base path from which to start searching for the CSV file
115 $searchBasePath = "./"
116
117 # Calculate the price
118 $price = get-Price -sla $sla -Flavour $Flavour -osInput $os -managed $managed -cloudzone $cloudzone -filePath $searchBasePath
119
120 return $price
121}
Now, let's create a zip file containing both the CSV file and the PowerShell script. The zipped file should be imported into the vRo action set with Type Zip:
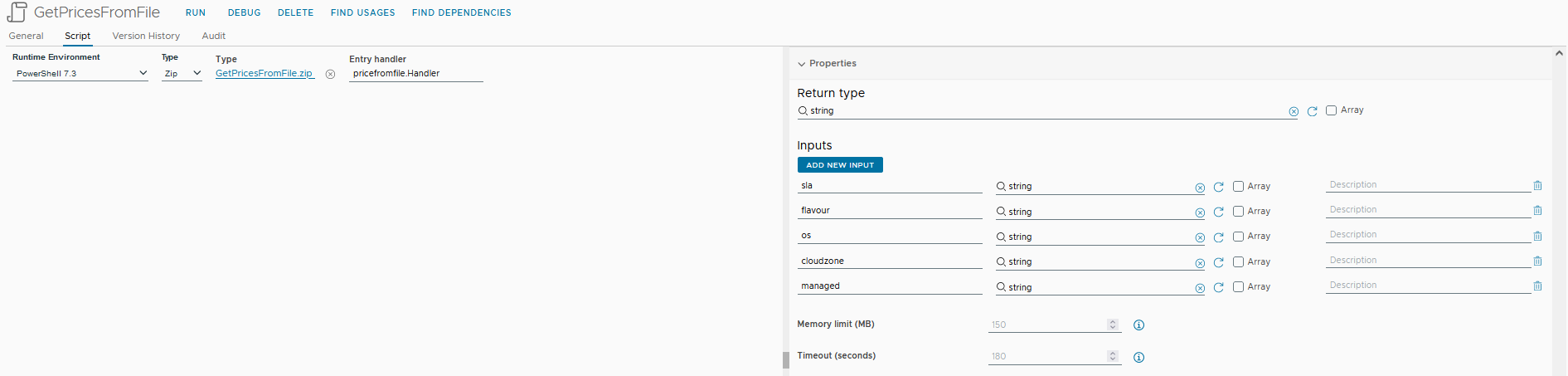
Note that the entry handler value should be entered as PS1__FILE__NAME.YOUR__HandlerFunction (In my case, pricefromfile.Handler).
Warning: The script mentioned above is for illustrative purposes and may need to be adapted to your own environment and needs.
Service Broker
Using vRo Action in Service Broker
Now we need to integrate our newly created Action in vRo into the Service Broker to display the output of our script that calculates prices.
To do this, after publishing the Blueprint inside the Service Broker, we create a Custom Form.
As the last block, we add a text element, changing the value from Constant to External and then selecting the name of the vRo Action we just created.
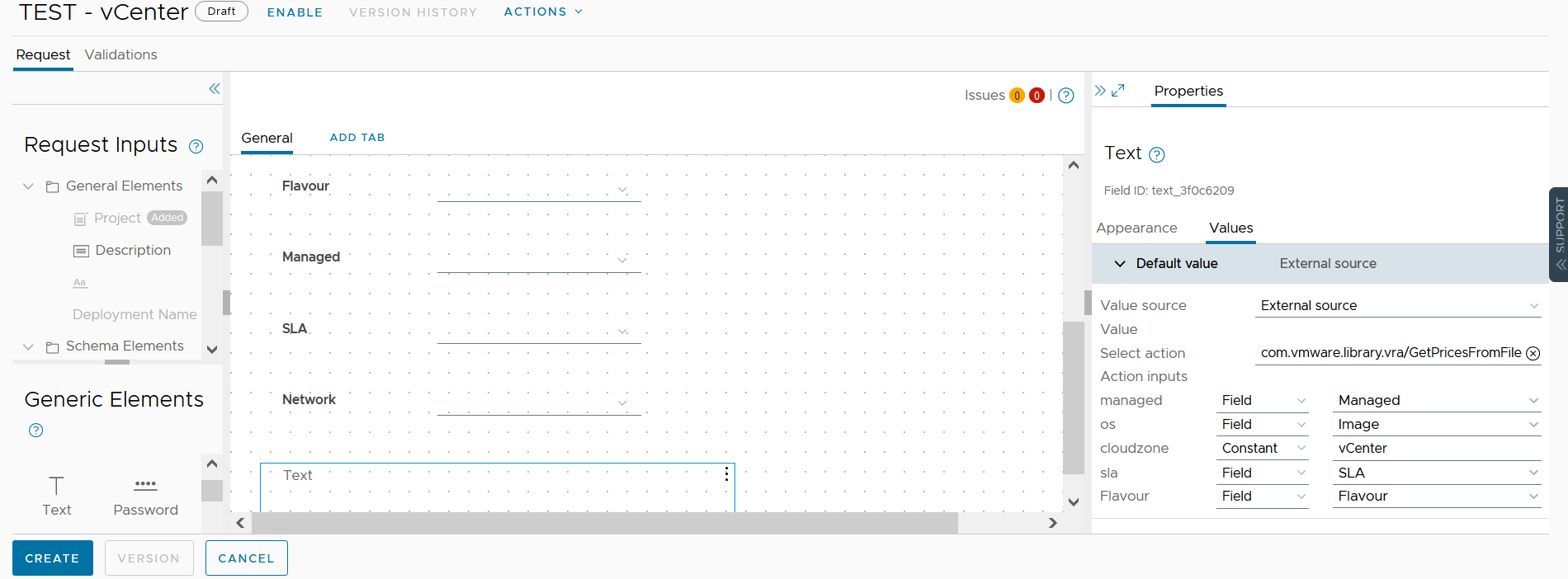
In this case, the CloudZone is entered as a Constant instead of a Field of the Blueprint. Before proceeding to save, we also need to insert a custom CSS, otherwise, the output text will be written all on the same line, whereas we want a more readable formatting.
To do this, click on Actions and then on Import CSS. The CSS code is really super simple:
1cf-text {
2 white-space: pre;
3}
Warning: This CSS will modify all the text-type elements you have added. It might cause some issues if you have multiple text fields.
After importing the CSS file, everything is ready! Click on 'Create', then 'Enable', and we can proceed with a test. After that, we'll need to do the same for the remaining Blueprints.
Notes
Output
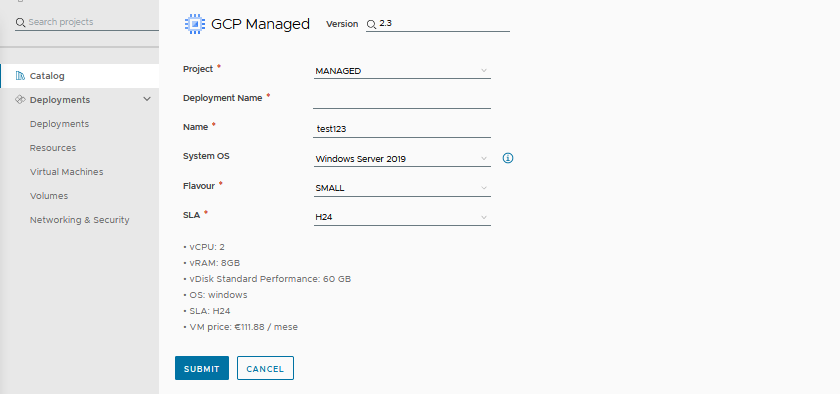
The script's output displays the following information: some details like vCPU and vRAM are calculated from the CSV file. Others, such as vDisk, are constants (this is because, for simplicity, the Blueprint templates have been customized to have the OS disk of the same size). This can also be modified if necessary.
- "• vCPU: $vcpu "
- "• vRAM: ${vram}GB "
- "• vDisk Standard Performance: 60 GB "
- "• OS: $os "
- "• SLA: $sla "
- "• vm price: €$priceTotal / month"